Pneumonia
Pneumonia
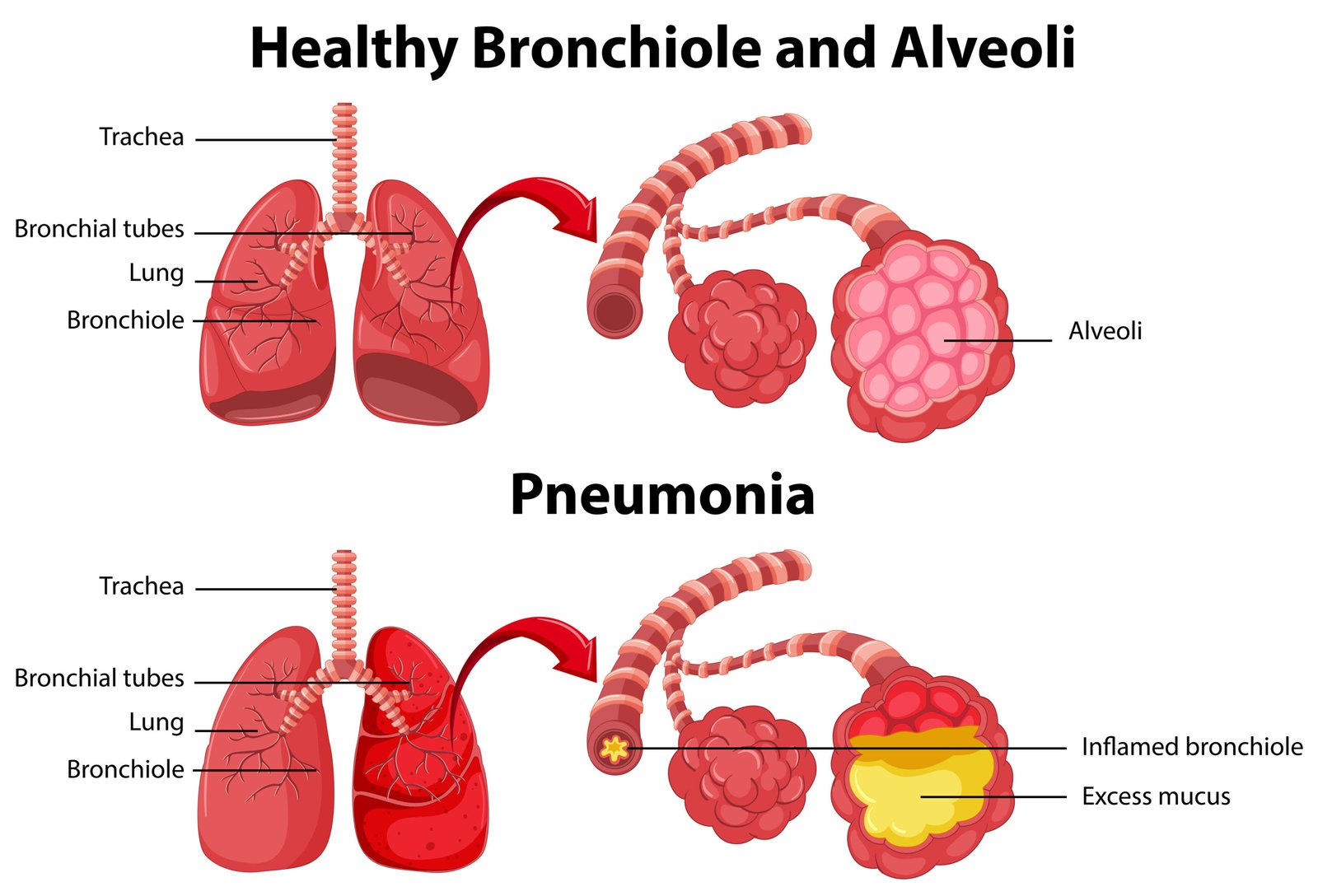
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that causes inflammation and fluid build-up in the air sacs. This can be caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Pneumonia can cause difficulty breathing, chest pain and cough, and may require hospitalization if severe.
Common symptoms
The symptoms of pneumonia in children can range from mild to severe.
- Cough (with or without mucus production)
- Fever
- Rapid breathing or difficulty breathing
- Wheezing or shortness of breath
- Fatigue or weakness
- Chest pain or discomfort, especially with coughing or breathing
- Loss of appetite
- Bluish lips or nails (in severe cases)
Infants and toddlers may experience irritability, difficulty feeding, and signs of respiratory distress like flaring nostrils or grunting while breathing.
Diagnosing Pneumonia in Children
A detailed medical history and physical examination is necessary to diagnose pneumonia and gauge its severity. Additional tests may include:
- Chest X-ray
- Blood tests
- Sputum culture or biofire panel
Treatment
Treatment for pneumonia depends upon the severity of infection, and the child’s overall condition. If the child is otherwise stable with mild symptoms, pneumonia can be managed on an out-patient basis with oral medications.
However, if the child has severe breathing difficulty or requires oxygen, hospitalization is required. Antibiotics and/or antivirals are the main group of medications along with supportive care.
Conditions Treated
- Adenoid Hypertrophy
- Allergic Rhinitis
- Asthma
- Breathing Difficulty
- Chest Pain
- Childhood Interstitial Lung Diseases (chILD)
- Chronic Cough
- Chronic Suppurative Lung Disease
- Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Noisy Breathing
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Pleural Effusion & Empyema
- Pneumonia
- Tuberculosis
- Wheezing
