Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Gastro-esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) occurs when stomach acid or contents flow backward into the esophagus, causing discomfort and potential long-term health issues. While it is normal for babies and infants to experience occasional reflux, persistent reflux in children can lead to GERD, a more serious condition that requires medical attention.
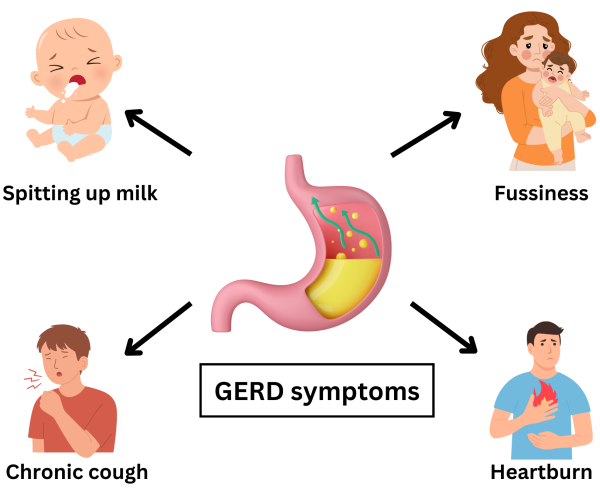
Common Symptoms of GERD in Children
GERD symptoms in children can vary depending on the age of the child and the severity of the condition.
Older children and adolescents may complain of one or more of the following:
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, often after eating or lying down
- Regurgitation: Food or sour liquid coming back into the mouth.
- Chronic cough, especially at night.
Symptoms seen in infants and young children with GERD include:
- Frequent vomiting or spitting up of milk
- Poor weight gain
- Irritability or fussiness
- Arching of back
- Recurrent wheezing or asthma-like symptoms
What Causes GERD in Children?
GERD occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the muscle between the esophagus and stomach, is weakened or relaxes abnormally. This allows stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus.
Several factors can contribute to GERD in children:
- In babies, GERD often occurs due to the immaturity of the LES. Most babies outgrow this as their sphincter muscle develops.
- Large meals or overfeeding can increase the risk of reflux.
- Obesity, especially excessive abdominal girth puts additional pressure on the stomach, which can push acid into the esophagus.
- Hiatal hernia: A condition where part of the stomach moves up into the chest cavity can increase the risk of reflux.
- Medications: Certain medications may relax the LES or irritate the esophagus, leading to GERD symptoms.
Diagnosing GERD in Children
Medical history usually provides clues to the diagnosis. Depending on the severity of symptoms, further tests may be needed, including:
– Esophageal pH Monitoring
– Upper GI Series (X-rays)
– Endoscopy
Treatment Options for GERD in Children
In most cases, the symptoms of GERD can be managed with lifestyle and dietary changes. Medications to reduce acid production in the stomach may be added. Severe cases that don’t respond to lifestyle measures and medications may need a surgery called fundoplication .
While occasional reflux is common, if your child experiences persistent symptoms that interfere with daily life, it’s imperative to consult a healthcare provider.
Conditions Treated
- Adenoid Hypertrophy
- Allergic Rhinitis
- Asthma
- Breathing Difficulty
- Chest Pain
- Childhood Interstitial Lung Diseases (chILD)
- Chronic Cough
- Chronic Suppurative Lung Disease
- Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Noisy Breathing
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Pleural Effusion & Empyema
- Pneumonia
- Tuberculosis
- Wheezing
