Asthma
Asthma
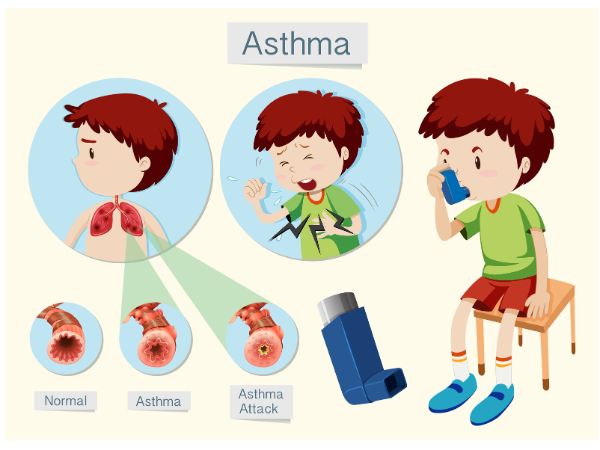
Common Symptoms of Childhood Asthma
- Cough : Persistent cough, particularly at night or early in the morning, often worse with exercise or exposure to triggers.
- Wheezing : A high-pitched whistling sound especially while exhaling.
- Shortness of Breath : Difficulty breathing or a sensation of being out of breath, particularly during physical activity or at night.
- Chest Tightness : A feeling of tightness or pressure in the chest, which can be accompanied by difficulty breathing.
In some cases, asthma symptoms may be mild and occur only during certain times, such as after exercise or exposure to an allergen. In other children, asthma can cause severe, frequent attacks. Most children have worsening of symptoms on exertion, hence they try to avoid activity.
Causes of Childhood Asthma
The exact cause of asthma is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the common causes and triggers of childhood asthma include:
- Genetics: Asthma often runs in families.
- Allergic reactions to pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or mould can trigger asthma symptoms in children who are sensitive to these allergens.
- Respiratory infections, especially viral infections such as the common cold or flu, can worsen asthma symptoms or trigger an asthma attack, particularly in younger children.
- Environmental exposure to air pollution, tobacco smoke, or strong odours can irritate the airways and increase the likelihood of asthma development.
- Chemical irritants: Exposure to chemicals found in cleaning products, perfumes, or paints can trigger asthma symptoms.
- Children who are overweight or obese may be at an increased risk of developing asthma or experiencing more severe asthma symptoms.
Diagnosing Childhood Asthma
- Diagnosis of asthma is mainly clinical, and is usually evident after a detailed history and examination by a qualified healthcare professional.
- A test called spirometry is usually performed in older children (typically over 5 years) to confirm the diagnosis and assess the baseline lung function.
- Some children with atypical symptoms may need additional tests such as chest X ray or CT scan of the chest to rule out alternative diagnoses.
- If allergies are suspected as triggers, an allergy test may be performed to identify specific allergens that may worsen asthma symptoms.
Management of Childhood Asthma
While asthma cannot be cured, it can be controlled with proper treatment. Inhaled steroids are the mainstay of asthma management. The best method to deliver inhaled steroids to airways is by use of inhalers. The goal of asthma treatment is to reduce inflammation, prevent asthma attacks, and help children lead a normal, active life. With regular use of controller medications, children can stay healthy and active while avoiding unnecessary asthma flare-ups.
Conditions Treated
- Adenoid Hypertrophy
- Allergic Rhinitis
- Asthma
- Breathing Difficulty
- Chest Pain
- Childhood Interstitial Lung Diseases (chILD)
- Chronic Cough
- Chronic Suppurative Lung Disease
- Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Noisy Breathing
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Pleural Effusion & Empyema
- Pneumonia
- Tuberculosis
- Wheezing
